[Source: Reuters]
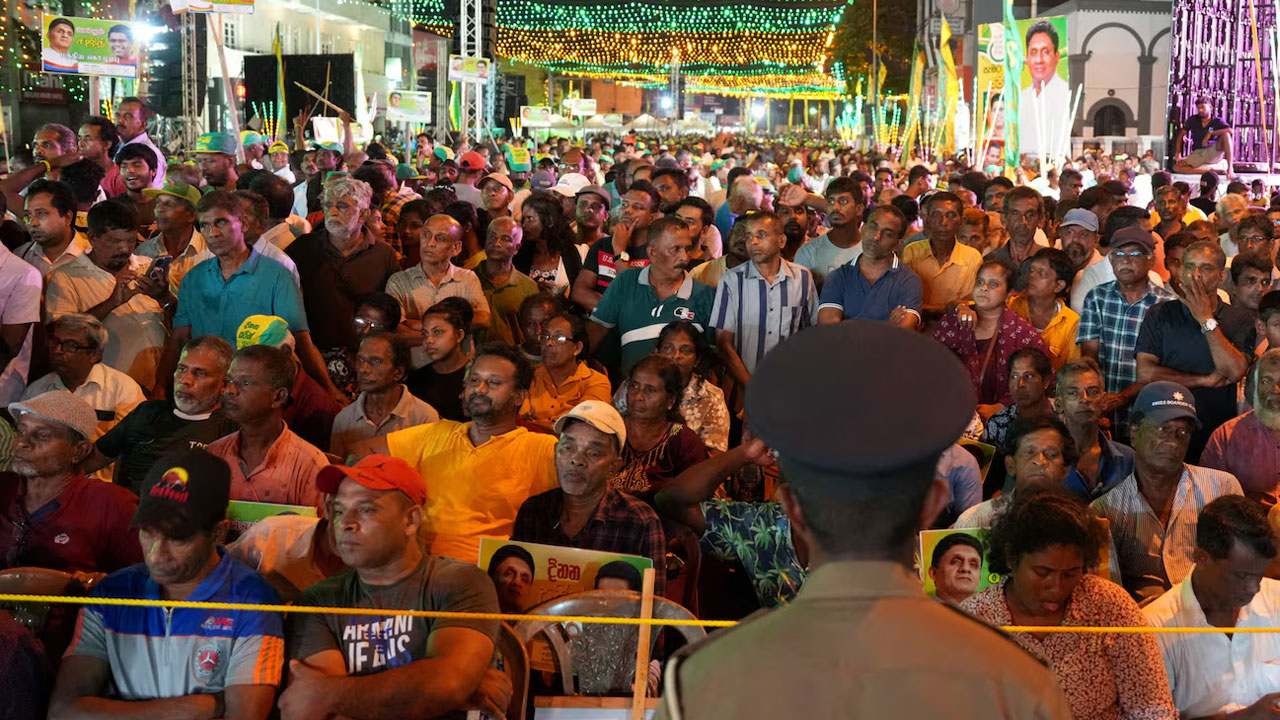
Millions of Sri Lankans were casting their votes on Saturday to select a president who will face the task of bolstering the South Asian country’s fragile economic recovery following its worst financial crisis in decades.
More than 17 million of Sri Lanka’s 22 million people are eligible to vote in an election that has shaped up to be a close contest between President Ranil Wickremesinghe, main opposition leader Sajith Premadasa and Marxist-leaning challenger Anura Kumara Dissanayake, who led in one recent opinion poll.
Citizens in the capital Colombo lined up early at polling booths, which were guarded by security personnel, as voting began at 7 a.m. It was proceeding peacefully across the island nation, according to local media.
Polls close at 4 p.m., with counting scheduled to start shortly afterward. The Election Commission is expected to announce the winner on Sunday.
Over 13,000 polling stations were set up across the country and 250,000 public officials were deployed to manage the election, R.M.L. Rathnayake, the head of Sri Lanka’s election commission, told Reuters.
This is the first election since Sri Lanka’s economy buckled in 2022 under a severe foreign exchange shortage, leaving the Indian Ocean island nation unable to pay for imports of essentials including fuel, medicine and cooking gas.
Thousands of protesters marched in Colombo in 2022 and occupied the president’s office and residence, forcing then-President Gotabaya Rajapaksa to flee and later resign.
Buttressed by a $2.9 billion bailout program from the International Monetary Fund, Sri Lanka’s economy has posted a tentative recovery but the high cost of living remains a core issue for many voters.
Although inflation cooled to 0.5% last month from a crisis high of 70%, and the economy is forecast to grow in 2024 for the first time in three years, millions remain mired in poverty and debt, with many pinning hopes of a better future on their next leader.
Whoever wins the election will have to ensure Sri Lanka sticks with the IMF program until 2027 to get its economy on a stable growth path, reassure markets, attract investors and help a quarter of its people climb out of crisis-caused poverty.
Sri Lanka’s ranked voting system allows voters to cast three preferential votes for their chosen candidates.
If no candidate wins 50% in the first count, there is a second round between the two frontrunners, with the preferential votes of other candidates redistributed, an outcome analysts say is likely given the close nature of the election.
Stream the best of Fiji on VITI+. Anytime. Anywhere.

 Reuters
Reuters