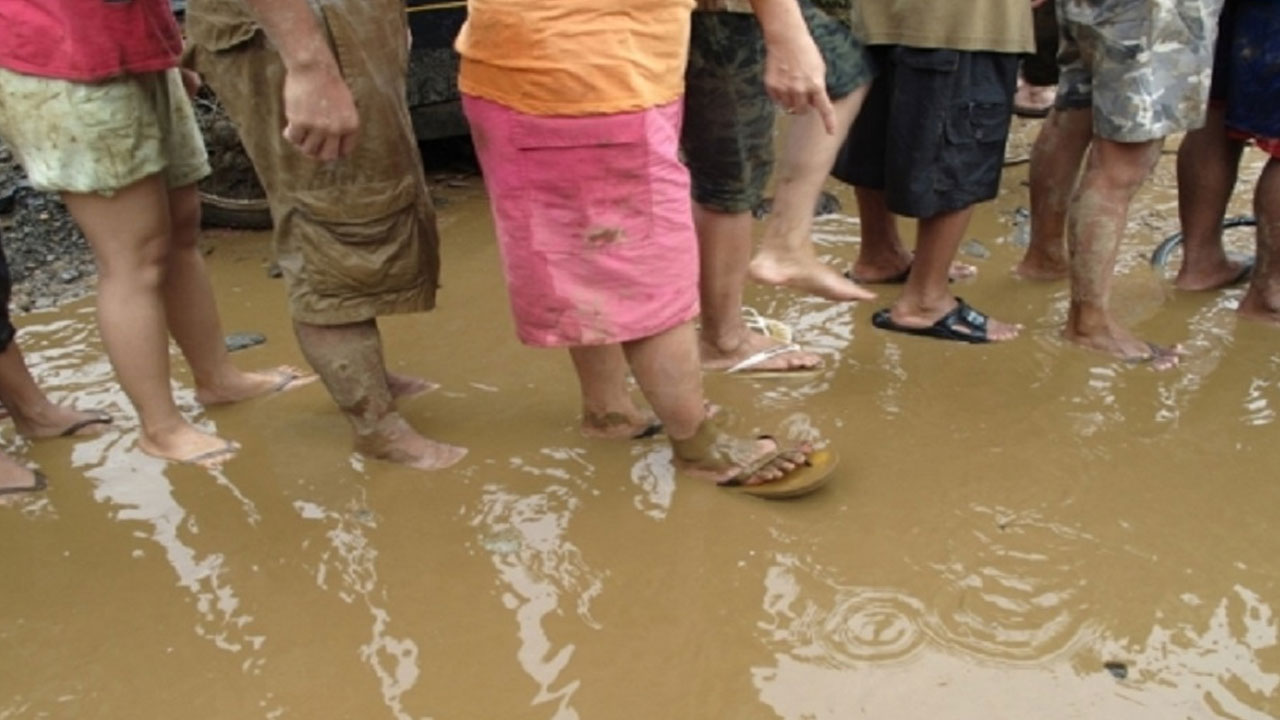
There has been a surge in leptospirosis cases in Kadavu.
The Ministry of Health says there have been a total of 23 reported cases this year.
It says 14 cases were reported over the last three weeks, and five of these cases were reported just this week.
According to the Health Ministry, 17 people with leptospirosis have been admitted to Vunisea Hospital in Kadavu this year, with an escalation in admissions in recent weeks.
Four people with severe leptospirosis were medically evacuated to the CWM Hospital in Suva over the last four weeks, with one death recorded.
The Health Ministry states that there are likely significantly more people with leptospirosis in Kadavu that have not presented to health facilities, as the challenging geographical layout of the island means that only people with the most severe form of the disease are being brought to be treated.
The Ministry’s Eastern Divisional Team is preparing surge support to increase the number of health personnel on the island to conduct direct community outreach.
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease that affects humans and animals and is spread through the urine of infected animals, which can contaminate water or moist soil for weeks or months.
Meanwhile, the Health Ministry has recorded 14 cases of typhoid in the provinces of Macuata and Bua in the Northern Division.
According to the Health Ministry, six cases were recorded in the last three weeks in Nasuva Village, Seaqaqa, with three recorded this week.
There have been no hospital admissions or deaths reported.
In Waikonadawa Settlement in Nasolo, Bua, five cases were recorded in the last three weeks.
There have been three admissions and no deaths reported in Nasolo.
The Ministry’s Northern Divisional Team is forming a taskforce to respond to these outbreaks, conducting necessary interventions such as door-to-door screening and awareness campaigns in the at-risk communities.
Typhoid fever is a common disease due to poor sanitation in some areas, people not washing their hands properly, and especially during and after the wet season, when flooding can spread the contaminated water to food crops and water sources.

 Shania Shayal Prasad
Shania Shayal Prasad