[Source: Reuters]
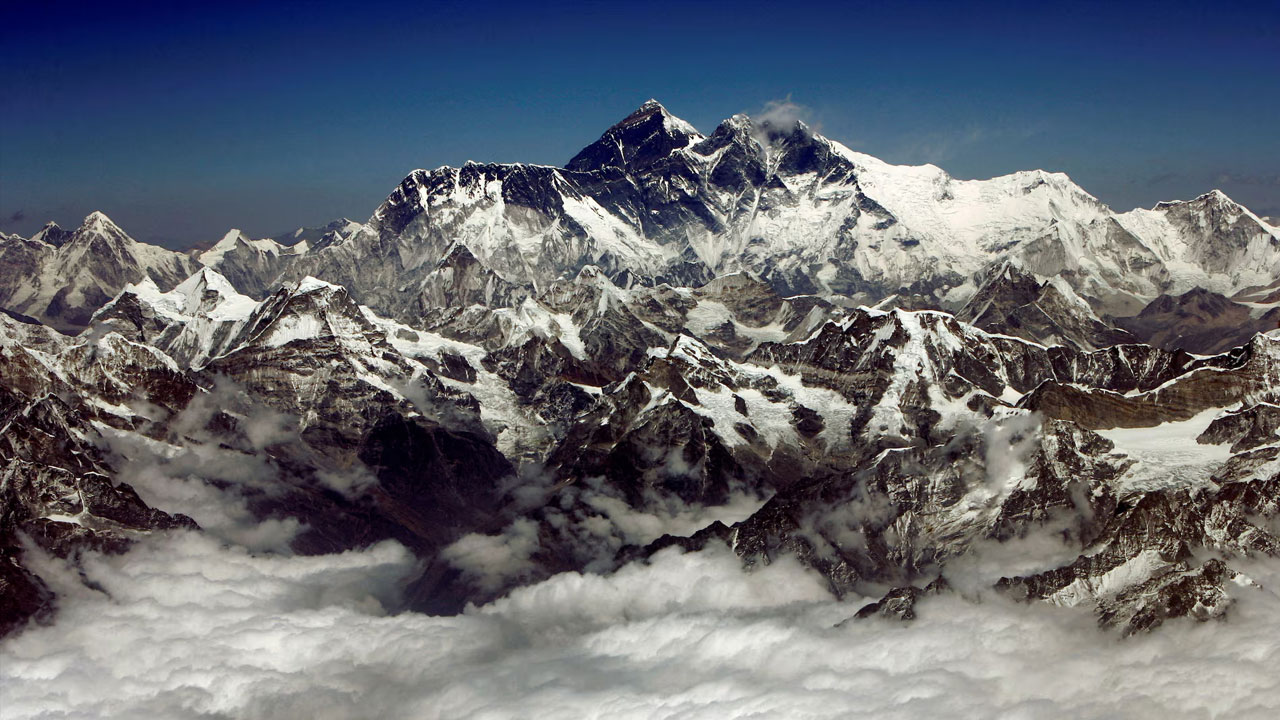
Mount Everest is Earth’s tallest mountain – towering 5.5 miles (8.85 km) above sea level – and is actually still growing.
While it and the rest of the Himalayas are continuing an inexorable uplift that dates back to their birth roughly 50 million years ago when the Indian subcontinent collided with Eurasia, Everest is growing more than expected from this alone. Scientists now think they know the reason why, and it has to do with the monumental merger of two nearby river systems.
Everest has gained roughly 49-164 feet (15-50 meters) in height due to this change in the regional river system, with the Kosi river merging with the Arun river approximately 89,000 years ago, the researchers estimated. That translates to an uplift rate of roughly 0.01-0.02 inches (0.2-0.5 millimeters) per year.
The geological process at work, they said, is called isostatic rebound. It involves the rise of land masses on Earth’s crust when the weight of the surface diminishes. The crust, Earth’s outermost layer, essentially floats atop a mantle layer made of hot, semi-liquid rock.
In this case, the merger of the rivers – more like a hostile takeover, with the Kosi subjugating the Arun as the rivers changed course over time – resulted in accelerated erosion that has carried off huge amounts of rock and soil, reducing the weight of the region near Everest.
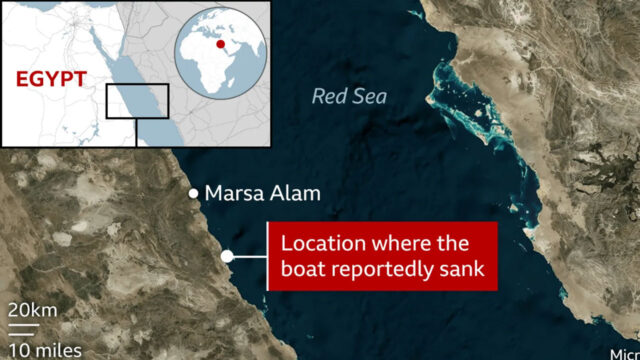
The main gorge of the merged river system is located approximately 28 miles (45 km) east of Everest.
The researchers, who used numerical models to simulate the evolution of the river system, estimated that isostatic rebound accounts for about 10% of Everest’s annual uplift rate.
This geological process is not unique to the Himalayas.
Study co-author Adam Smith, a University College London doctoral student in Earth sciences, said GPS measurements reveal the continued rising of Everest and the rest of the Himalayas.
This uplift outpaces the continued surface erosion caused by factors such as wind, rain and river flow. As this erosion continues, Everest’s uplift rate from isostatic rebound may increase, Smith said.
Neighboring peaks including Lhotse, the world’s fourth highest, and Makalu, the fifth highest, also get a boost from the same process. Lhotse is experiencing an uplift rate similar to Everest. Makalu, situated closer to the Arun, has a slightly higher uplift rate.
Earth’s rigid outer part is divided into colossal plates that move gradually over time in a process called plate tectonics, with the Himalayas rising following a collision between two plates.
Everest, also called Sagarmatha in Nepali and Chomolungma in Tibetan, is situated on the border between Nepal and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It was named for George Everest, a 19th century British surveyor in India.

 Reuters
Reuters